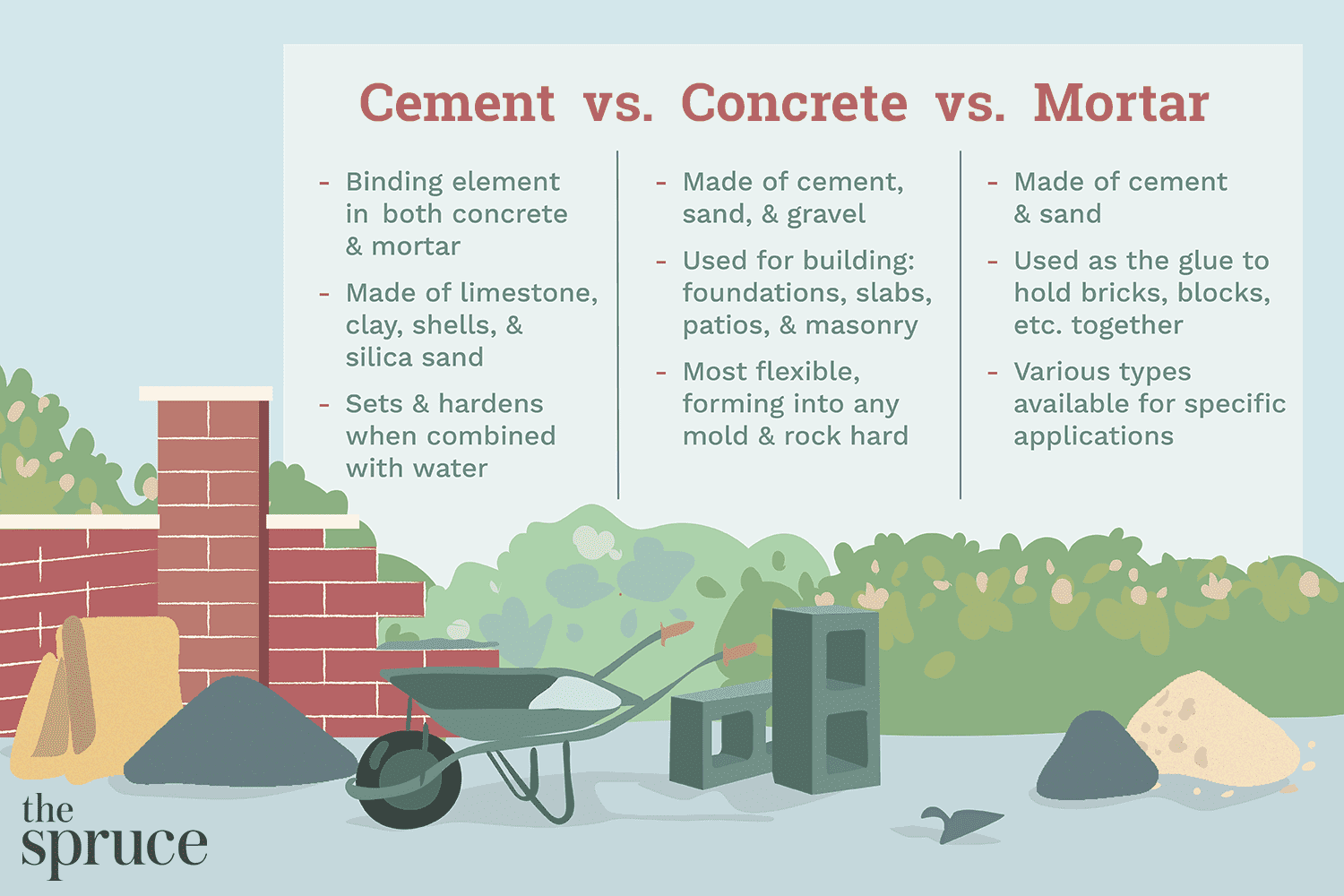
Masonry cement is a blend of Portland cement, plasticizers, and air-entraining agents, ideal for constructing masonry units. Mortar cement is a mix of Portland cement and hydrated lime, specifically designed for creating mortar for laying bricks and blocks.
Masonry cement offers higher bond strength for structural applications, while mortar cement provides better workability and water retention for laying bricks and blocks efficiently. Both types of cement are crucial for successful masonry projects, each serving a specific purpose in ensuring the durability and integrity of the structure.
Understanding the differences between masonry cement and mortar cement is essential for selecting the right material for your construction needs.
Introduction To Masonry And Mortar Cement
Discover the distinction between masonry cement and mortar cement, essential components in construction projects. While masonry cement is versatile for various applications, mortar cement offers superior bonding strength for brick and stone work. Understanding their unique properties is crucial for achieving durable and stable structures.
Introduction to Masonry and Mortar Cement Masonry cement and mortar cement are two essential materials used in construction projects. Masonry cement is designed for use in brick, block, and stone masonry, providing durability and strength to the structure. On the other hand, mortar cement is specifically formulated for use in bonding masonry units, creating a strong and cohesive bond between them. Both types of cement consist of similar key ingredients, including Portland cement, limestone, and other additives. However, they differ in their proportions and properties. Masonry cement contains a higher percentage of Portland cement, making it ideal for load-bearing applications. Mortar cement, on the other hand, has a higher lime content, providing greater workability and adhesive properties. In historical context, the use of masonry and mortar cement dates back centuries, with evidence of their use in ancient structures around the world. These materials have stood the test of time, showcasing their reliability and effectiveness in construction. Overall, understanding the distinctions between masonry and mortar cement is crucial for choosing the right material for your specific construction needs. Whether it’s for building a sturdy wall or creating a long-lasting structure, the right cement choice can make all the difference in the success of your project.
The Composition Of Masonry Cement
Masonry cement and mortar cement are both essential for construction, each with its own unique composition and characteristics. Masonry cement is a blended mix of portland cement, plasticizers, and air-entraining agents, designed for use in masonry construction. On the other hand, mortar cement is a specially formulated blend of portland cement, lime, and other additives to create a strong, durable mortar for brick, block, and stone masonry. The main components of masonry cement include portland cement, hydrated lime, and other ingredients that enhance workability and performance. Additives play a crucial role in improving the workability, strength, and durability of masonry cement, ensuring it meets the specific requirements of masonry construction projects.
The Composition Of Mortar Cement
Masonry cement and mortar cement are both crucial for construction projects, each with its own unique composition and applications. Mortar cement typically consists of a blend of Portland cement, hydrated lime, and sand. These core ingredients create a durable and workable material that is ideal for joining bricks, blocks, and stones.
Lime plays a significant role in mortar cement, enhancing workability and water retention while also contributing to the overall strength and durability of the finished product. This natural mineral helps prevent cracking and ensures that the mortar remains pliable for a longer duration, making it easier to work with during construction.
Comparing Performance And Applications
Masonry cement and mortar cement each have distinct performance and application differences. Masonry cement is designed for use in mortar for masonry construction, while mortar cement is formulated specifically for bonding masonry units. Understanding these differences is crucial in choosing the right material for a specific construction project.
| Strength and Durability | Suitable Use Cases |
|---|---|
| Masonry cement and mortar cement both offer excellent strength and durability for various construction projects. | – Masonry cement is commonly used for bricklaying, blockwork, and stonework. Its high compressive strength makes it ideal for load-bearing applications. |
| – Mortar cement, on the other hand, is designed specifically for masonry mortar, which is used to bond bricks, stones, or concrete blocks together. It provides good workability and adhesion. | – Masonry cement is suitable for projects that require high strength and resistance to harsh weather conditions. |
| – Mortar cement is often used for non-load-bearing applications such as plastering, rendering, and pointing. | – Both types of cement can be utilized in residential, commercial, and industrial construction projects. |
Workability And Setting Time
Masonry cement and mortar cement differ in terms of workability and setting time. Masonry cement offers improved workability, making it easier to handle and spread, while mortar cement provides a faster setting time, allowing for quicker construction projects. These distinctions make each type of cement suitable for specific applications in the field of masonry and construction.
| Workability and Setting Time |
| Masonry cement offers excellent workability due to its smooth texture, making it easier to spread and shape. It also has a longer setting time, allowing for more flexibility during construction. |
| Ease of Use |
| When it comes to ease of use, mortar cement is advantageous as it requires only the addition of water. This simplifies the mixing process and makes it more convenient for various applications. |
| Curing Process |
| Both types of cement require a curing process to reach their maximum strength. Masonry cement typically needs a longer curing period compared to mortar cement, which can influence project timelines. |
Environmental Impact And Sustainability
Masonry cement and mortar cement have varying environmental impacts and sustainability. Masonry cement is a blend of Portland cement and ground limestone, while mortar cement is a mix of Portland cement, hydrated lime, and sand. Both have different compositions, affecting their carbon footprint and durability.
| Energy Consumption | Recyclability and Eco-friendliness |
| Masonry cement typically requires higher energy consumption for production. | Mortar cement is more recyclable and environmentally friendly due to its composition. |
| It is essential to consider energy-efficient options to reduce environmental impact. | Choosing materials with higher recyclability promotes sustainability in construction practices. |
Cost Considerations
Comparing masonry cement vs. mortar cement involves cost considerations. Masonry cement can cost more due to its blend of Portland cement, while mortar cement is a more affordable option, made with hydrated lime and masonry sand. Understanding the cost differences can help in choosing the most suitable option for your project.
| Price Comparison: | Factors Influencing Cost: |
| Masonry cement usually costs less than mortar cement. | Amount needed, brand, and location affect overall cost. |
| Quality varies, influencing the price difference between the two. | Differences in strength and durability also impact pricing. |
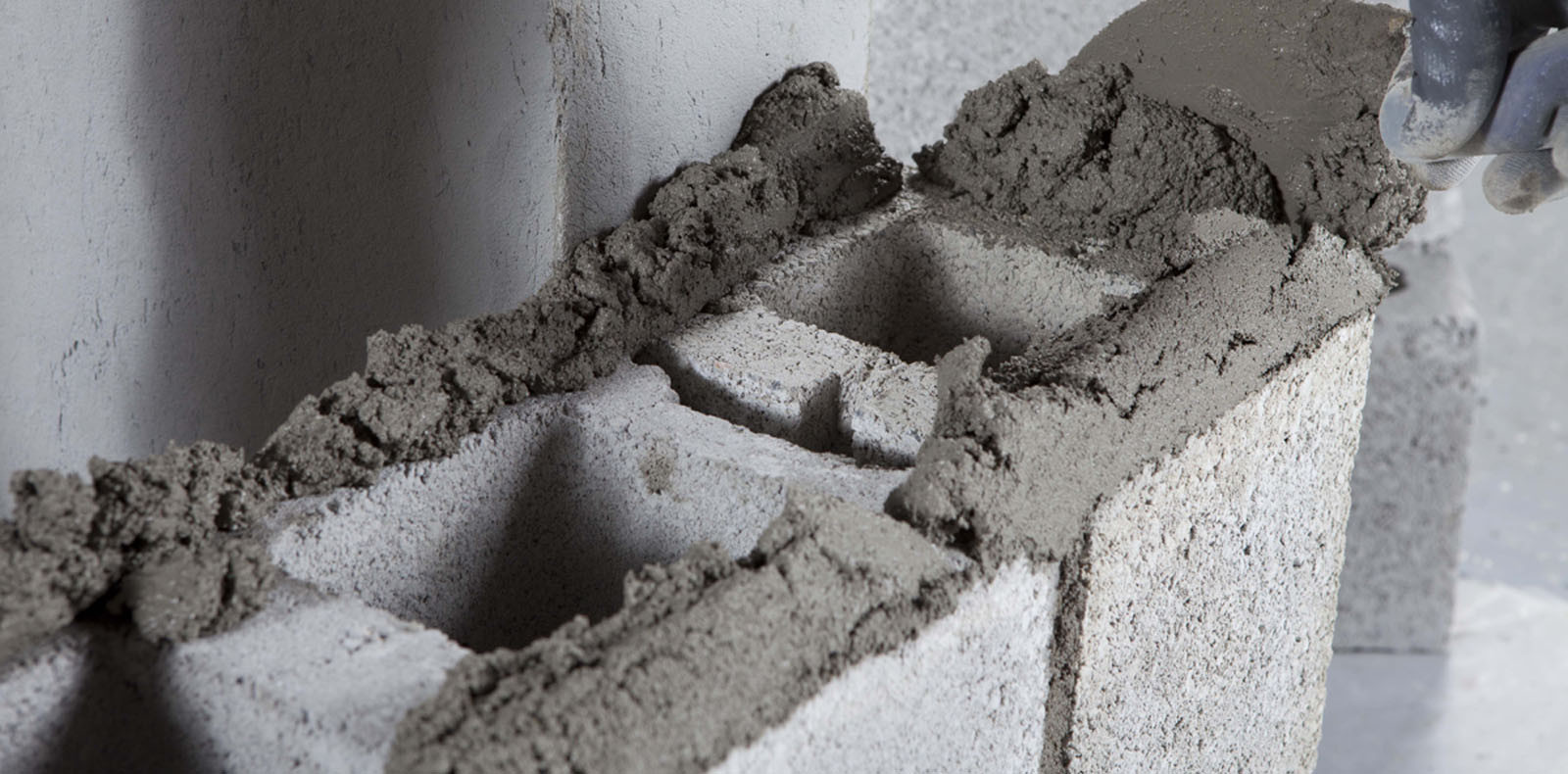

Making The Right Choice For Your Project
Choosing the right cement for your masonry project requires careful consideration. Understand the differences between masonry cement and mortar cement to ensure optimal results. Make an informed choice for a successful outcome.
| Masonry Cement | Mortar Cement |
| Contains plasticizers for workability | For binding bricks and stones |
| Higher compressive strength | Used for stucco and plaster |
| Meets ASTM C91 standards | Meets ASTM C1329 standards |
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/recommended-guide-for-selection-of-mortar-mix-type-844821-new-da021ac214d74f659a3959e812a65eab.png)
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Masonry Cement?
Masonry cement is a type of cement that is specifically formulated and manufactured for use in masonry construction. It is a blend of Portland cement, hydrated lime, and other materials.
What Is Mortar Cement?
Mortar cement is a type of cement that is specifically designed for use in masonry mortar. It is a mixture of Portland cement, hydrated lime, and other materials.
What Is The Difference Between Masonry Cement And Mortar Cement?
The main difference between masonry cement and mortar cement is the blend of materials used to make them. Masonry cement is designed for use in masonry construction, while mortar cement is designed for use in masonry mortar.
Can Masonry Cement Be Used In Place Of Mortar Cement?
No, masonry cement should not be used in place of mortar cement. Each type of cement is formulated for specific use, and using the wrong type of cement can result in poor performance and potential structural issues.
Conclusion
To sum up, both masonry cement and mortar cement have their own unique characteristics and uses in construction projects. Masonry cement is ideal for use in brick, block, and stone masonry, while mortar cement is used for mixing mortar for laying brick, block, and stone.
It is important to understand the differences between the two and to choose the appropriate cement for your specific project. Always consult with a professional to ensure you are using the correct materials for your construction needs.